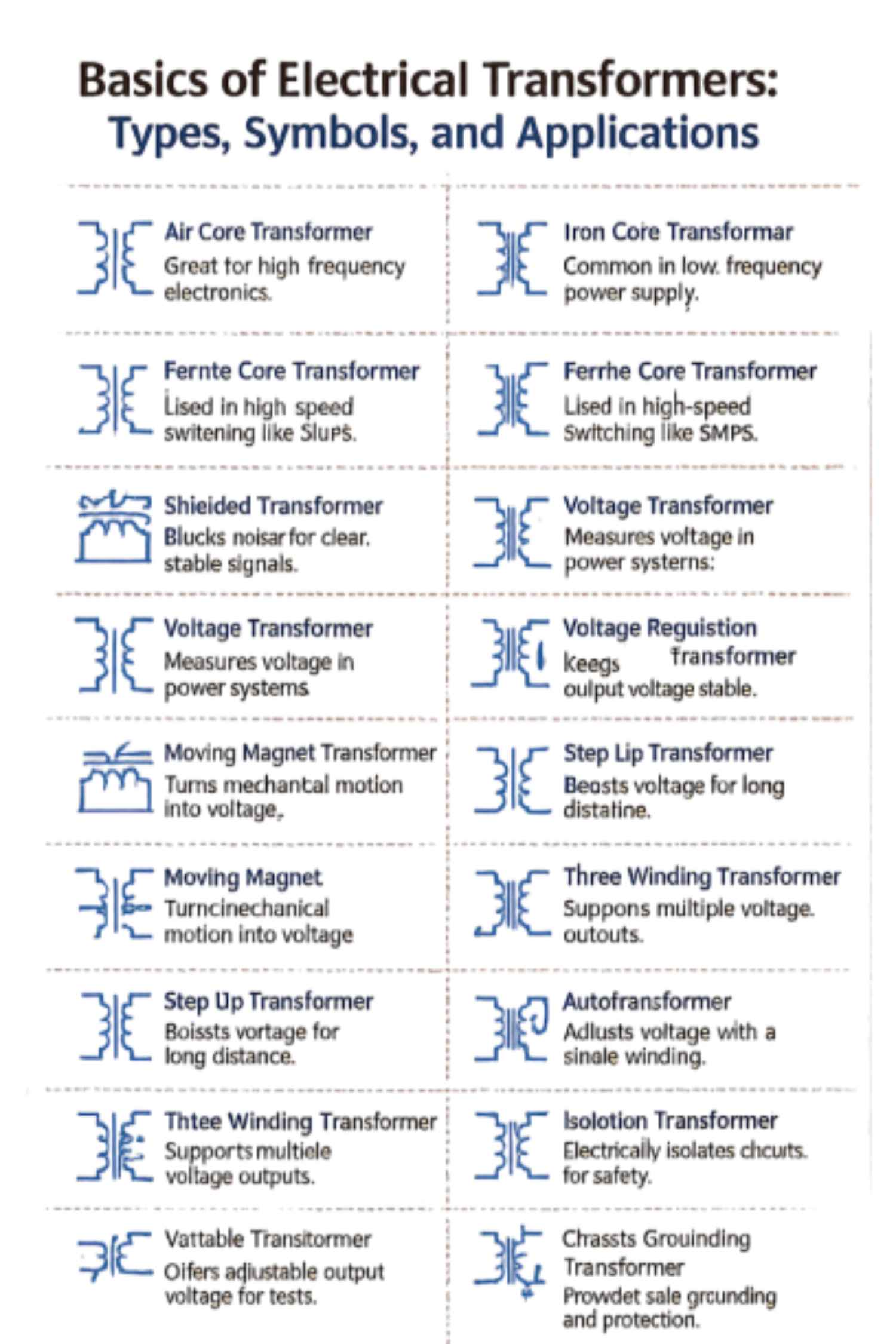
Key Transformer Types and Their Applications
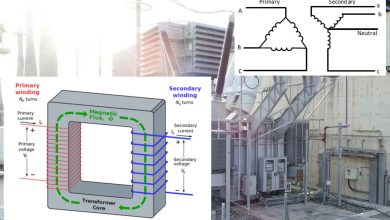
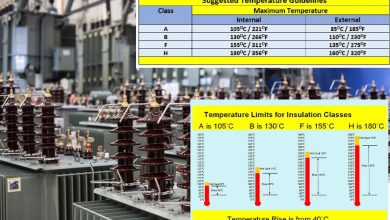
Transformers are fundamental components in electrical and electronic systems, enabling efficient power transmission, voltage regulation, and signal isolation. Depending on their construction, core material, and operating principles, transformers are designed for specific applications ranging from power distribution to precision measurement. Below is an overview of the most important transformer types and their roles in modern electrical systems.
1. Air Core Transformer
An air-core transformer uses air as the medium for magnetic flux rather than a solid core. This design eliminates core losses, making it ideal for high-frequency applications such as radio frequency (RF) circuits, where stable inductance at high frequencies is critical.
2. Iron Core Transformer
Iron-core transformers use laminated iron sheets to enhance magnetic coupling between the windings. They are widely used in low-frequency power circuits, such as mains power systems, due to their high efficiency and reliable energy transfer.
3. Ferrite Core Transformer
Ferrite-core transformers are built with ferrite materials that offer low losses at high frequencies. These transformers are commonly found in switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) and other high-speed switching applications.
4. Laminated Core Transformer
By stacking thin, laminated sheets, this transformer design significantly reduces eddy-current losses. Laminated core transformers are used in power systems to ensure safe, efficient, and long-term electrical energy transfer.
5. Shielded Transformer
Shielded transformers include electromagnetic shielding to minimize electrical noise and interference. They are especially useful in sensitive electronic and signal-processing equipment that requires stable, clean power.
6. Voltage Transformer (VT)
Voltage transformers step down high system voltages to safe, measurable levels. They are primarily used for voltage measurement, monitoring, and protection in power systems while maintaining a constant system frequency.
7. Current Transformer (CT)
Current transformers reduce high currents to lower, measurable values for monitoring and protection. They play a vital role in power-flow sensing and energy-management systems.
8. Voltage Regulation Transformer
Designed to maintain a constant output voltage, this transformer compensates for load variations. It ensures consistent and reliable power delivery in electrical networks.
9. Step-Up Transformer
A step-up transformer increases the input voltage without changing the operating frequency. These transformers are crucial in long-distance power transmission, where higher voltages reduce energy losses.
10. Step-Down Transformer
Step-down transformers lower voltage levels to make electricity safe for end-use equipment. They are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial power supplies.
11. Three-Winding Transformer
This transformer features three separate windings, allowing multiple output voltage levels. It is commonly used in industrial power distribution systems that require flexible voltage options.
12. Autotransformer
An autotransformer uses a single winding for both primary and secondary functions. It provides a variable-voltage output with high efficiency and is often used for voltage adjustment and motor starting applications.
13. Isolation Transformer
Isolation transformers electrically separate the input and output circuits while transferring power at the same voltage level. They enhance safety and protect equipment from electrical faults and noise.
14. Variable Transformer
Also known as a variac, this transformer allows adjustable output voltage at a constant frequency. It is commonly used in laboratories, testing environments, and control applications.
15. Saturable Reactor Transformer
This transformer regulates AC power by controlling magnetic saturation. It is used in applications that require smooth control of voltage or current.
16. Moving Magnet Transformer
Moving magnet transformers convert mechanical motion into voltage variations. They are often used in sensing and transducer applications where mechanical movement must be translated into electrical signals.
17. Current Regulation Transformer
Designed to maintain a stable current output, this transformer is essential in sensitive electronic systems where precise current control ensures balanced and reliable power delivery.
18. Chassis Grounding Transformer
This transformer enhances safety by ensuring proper grounding of electrical equipment. It helps control fault currents and protects both users and devices from electrical hazards.
Each transformer type serves a specific purpose, optimized for frequency range, power level, and application environment. Understanding these transformer variations helps engineers and technicians choose the right solution for efficient, safe, and reliable electrical system design.