Transformer Rating nameplate
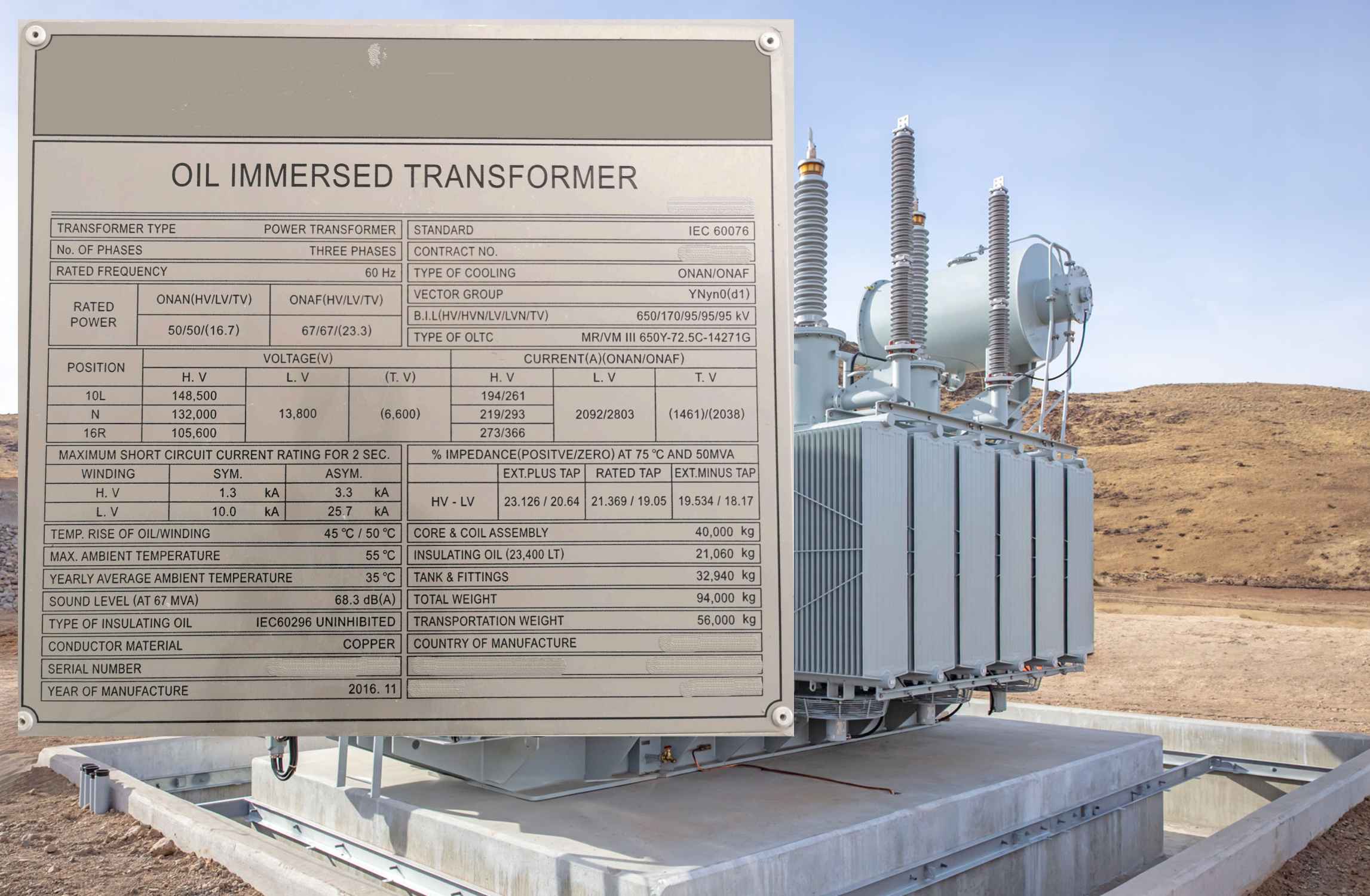
The transformer nameplate is a critical information resource for a device that is a fundamental component of the electrical power infrastructure. It provides essential specifications governing the safe and effective operation of the unit.
Key Nameplate Parameters:
I. Manufacturer Identification
Denotes the entity responsible for the transformer’s design and fabrication.
2. Insulation and Cooling Method
The designation “Oil-Immersed” specifies that the primary insulation and cooling medium is dielectric oil. This distinguishes it from alternative technologies, such as gas-insulated (e.g., sulfur hexafluoride, SF₆) or dry-type transformers, which employ solid insulation, such as cast resin.
3. Functional Classification
The classification as a “Power Transformer” indicates its intended application in the transmission or primary distribution network for high-power voltage transformation, as opposed to smaller distribution or control transformers.
4. Phase Configuration
Specifies a three-phase construction. While it is common for all three windings to be housed within a single tank, applications at extra-high voltage (EHV) with very high power ratings often employ a bank of three single-phase transformer units connected to form a three-phase system. This approach offers advantages in manufacturing, transport, and redundancy.
5. Rated Frequency
Defines the nominal system frequency (e.g., 60 Hz, 50 Hz) for which the transformer’s magnetic core and loss characteristics are designed. Operation at a different frequency may lead to core saturation or excessive losses.
6. Rated Power (kVA or MVA)
This is the apparent power output the transformer is designed to deliver continuously under specified conditions without exceeding permissible temperature rises. The rating is assigned to each winding voltage level. Adherence to this rating is paramount to prevent insulation degradation due to overheating caused by excessive current, thereby ensuring operational longevity and reliability.